Flat feet in children: what they are, when to worry, and how to treat them at home
Have you noticed that your child places their whole foot flat on the ground when walking, wears out their shoes unevenly, gets tired easily, or complains of pain after walking or playing sports? In many cases, these signs may be related to pediatric flat feet, a common foot condition during childhood which, although often benign, requires medical assessment when it causes symptoms like those described.
At Equipo Médico Ordovás, we offer a pediatric orthopedic home-visit service in Madrid, led by a specialist in musculoskeletal development in children. This allows for an accurate diagnosis of what is normal versus what is not, without the need for travel, in a calm and familiar environment.
What are flat feet in children?
Flat feet (pes planus) are a foot shape in which the medial arch is reduced or absent, causing much or all of the sole to come into contact with the ground when standing.
In young children, flat feet are usually physiological and flexible, as the arch has not yet fully developed. In fact, most babies and toddlers have flat feet, and in many cases the arch appears naturally between the ages of 5 and 8 years.
A problem may arise when:
Flat feet persist beyond the expected age and are symptomatic
The foot is not flexible on examination
Pain is present
Flat feet are associated with other abnormalities
What are the most common causes of pediatric flat feet?
The causes of flat feet are varied and depend largely on the child’s age. The main contributing factors include:
Normal development
This is the most common situation and involves an early absence of the arch. It occurs in most young children because the arch has not yet visibly formed. It may be due to a fat pad in the arch area and natural ligament laxity. This type of flat foot, known as flexible or physiological flat foot, is considered a normal stage of development.
Genetic predisposition
There is a significant hereditary component. If one or both parents have flat feet, the likelihood that the child will develop them is higher. This is often related to inherited ligament laxity or a particular bone structure.
Muscle hypotonia or ligament laxity
Weakness of the intrinsic foot and leg muscles, or excessive elasticity of the ligaments supporting the arch (hypermobility), can prevent the arch from forming or being maintained properly. Ligament laxity may be part of a generalized joint hypermobility syndrome.
Overweight
Increased mechanical load on the weight-bearing structures of the foot places extra stress on the ligaments and tendons of the arch. Excess weight can accelerate muscular and ligament fatigue, contributing to arch collapse and related symptoms.
Associated medical conditions or foot bone abnormalities
Flat feet may also be linked to other underlying diseases or structural bone alterations.
A pediatric orthopedic specialist can determine whether flat feet are part of normal development or whether specific follow-up and treatment are required. The key is to assess whether the foot is flexible or rigid and whether symptoms are present.
What are the consequences of flat feet?
Many children have no symptoms. However, when flat feet are rigid, associated with overweight, or accompanied by a shortened Achilles tendon, they can cause problems that affect quality of life and physical activity.
Common symptoms of symptomatic flat feet include:
Foot pain, especially in the arch area, due to excessive strain on ligaments and tendons
Fatigue when walking or running, as foot and leg muscles work inefficiently to stabilize gait
Clumsiness or avoidance of physical activity, due to reduced stability
Knee strain and pain, caused by altered foot alignment (excessive pronation)
Postural changes, such as slouched posture, rounded shoulders, knock-knees, or increased lumbar lordosis
How are flat feet diagnosed during a home visit?
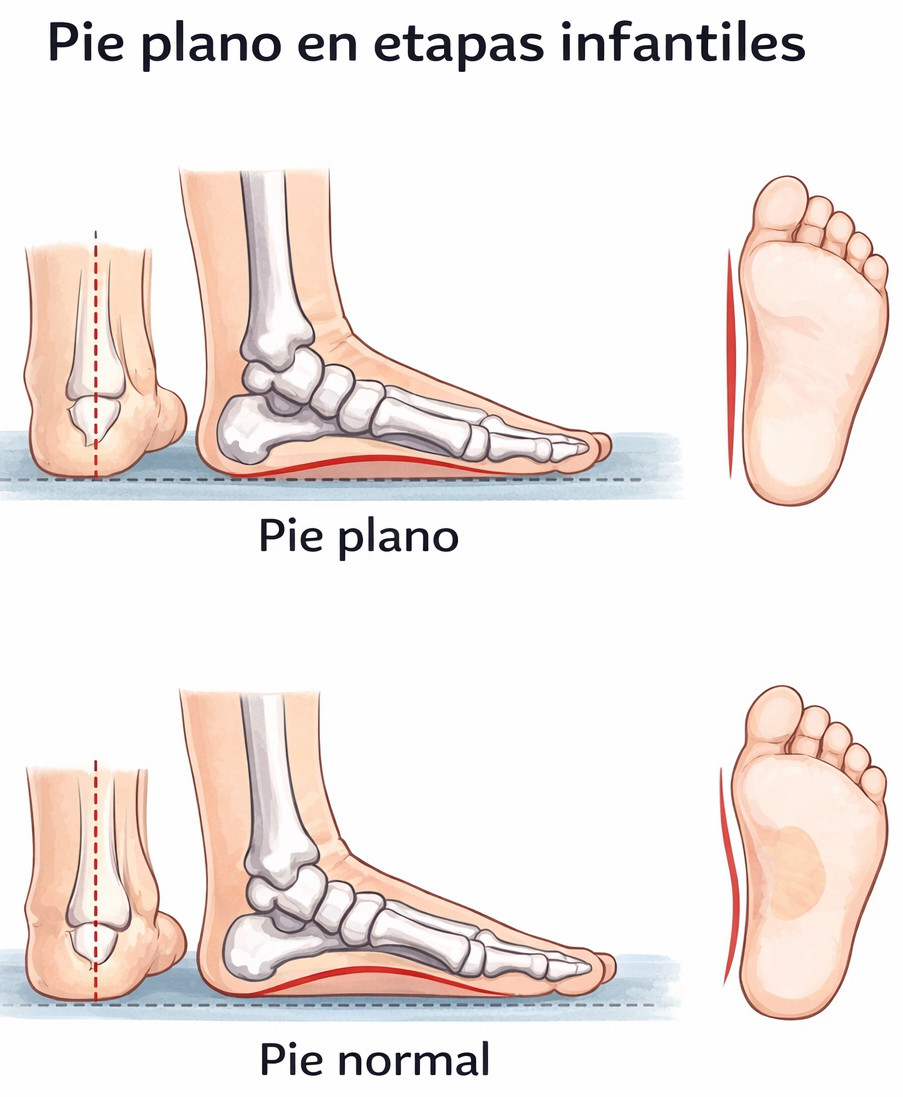
Assessment of foot support with and without weight-bearing, observing how the foot behaves when standing, walking, sitting, or lying down
Gait and posture analysis, observing walking patterns, limping, leg rotation, asymmetries, and signs of scoliosis or kyphosis
Evaluation of arch flexibility and joint mobility, to differentiate between flexible and rigid flat feet
Assessment of ankle, knee, and hip alignment, checking for bow legs, knock-knees, ankle position, and hip rotation
Review of everyday footwear, including shoe type, wear patterns, and suitability for the child’s age and activity level
How are flat feet diagnosed during a home visit?
A pediatric orthopedic home visit avoids unnecessary travel and allows for a thorough musculoskeletal assessment in a relaxed, familiar setting. Evaluation includes:
Assessment of foot support with and without weight-bearing, observing how the foot behaves when standing, walking, sitting, or lying down
Gait and posture analysis, observing walking patterns, limping, leg rotation, asymmetries, and signs of scoliosis or kyphosis
Evaluation of arch flexibility and joint mobility, to differentiate between flexible and rigid flat feet
Assessment of ankle, knee, and hip alignment, checking for bow legs, knock-knees, ankle position, and hip rotation
Review of everyday footwear, including shoe type, wear patterns, and suitability for the child’s age and activity level
How can flat feet be treated?
Treatment is individualized and depends on the child’s age, symptoms, and type of flat foot:
Observation and follow-up: for flexible, painless flat feet, as natural arch development is expected. Parents are reassured, regular check-ups are scheduled, and free physical activity and barefoot walking are encouraged.
Targeted exercises: physiotherapy is helpful when muscle tightness or tendon shortening is present.
Appropriate footwear: comfortable, functional shoes with a flexible sole, stable heel, and wide toe box. Rigid shoes or prefabricated arches should be avoided.
Custom orthotic insoles (only when necessary): they do not correct the foot but help improve alignment and relieve symptoms. They must be personalized and based on gait and footprint analysis.
Postural education and monitoring: posture guidance and regular follow-up to adapt treatment as the child grows.
Surgery is considered only in very specific cases, when conservative treatment has completely failed and flat feet cause persistent, disabling pain or functional limitation, or when underlying structural abnormalities are present.
What happens if flat feet are not treated?
When flat feet are symptomatic, lack of proper evaluation and follow-up can lead to long-term musculoskeletal problems due to chronic biomechanical imbalance, including:
Chronic foot or leg pain, such as heel pain (plantar fasciitis), Achilles or posterior tibial tendinitis, and metatarsalgia
Knee and hip pain, caused by misalignment spreading upward from the foot
Reduced physical activity, leading to a more sedentary lifestyle and potential weight gain
Abnormal gait patterns, with inefficient walking and increased energy expenditure
Progressive postural problems, including postural scoliosis, increased lordosis or kyphosis, back pain, and toe deformities such as bunions or hammer toes
Early detection is key, especially in growing children. Addressing the problem in time can normalize foot biomechanics, prevent pain, and avoid long-term complications.
When should you consult a pediatric orthopedic specialist?
Seek medical evaluation if your child shows:
Persistent or recurrent pain in the feet, ankles, legs, or lower back
Easy fatigue or reduced endurance compared to peers
Postural problems when standing or walking
Marked or uneven shoe wear
Early assessment can rule out underlying conditions and, if needed, initiate treatments such as custom insoles or specific exercises to improve your child’s quality of life and motor development.
Benefits of home diagnosis and treatment
If you suspect your child may have flat feet or difficulty walking, Equipo Médico Ordovás offers pediatric orthopedic home visits in Madrid. Home care provides:
Assessment in the child’s usual environment
Reduced stress and anxiety
Avoidance of unnecessary travel
Easier long-term follow-up
Request a home evaluation. A specialized examination without leaving home can make a real difference in your child’s future development and well-being.